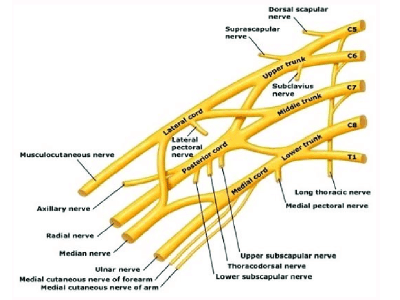
Brachial Plexus
Brachial Plexus
Understanding Brachial Plexus Injuries: Nerve Damage and Rehabilitation
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that extends from the neck into the arm, controlling movement and sensation. Injuries to this network, often caused by trauma or stretching during childbirth, can result in various degrees of impairment in the affected limb. Understanding the nature of these injuries, their impact, and available treatments is essential for affected individuals and their caregivers.
Types of Brachial Plexus Injuries
Brachial plexus injuries vary in severity, classified according to the extent of nerve damage:
- Neuropraxia: The mildest form, involving temporary nerve compression or stretching, leading to numbness or weakness.
- Axonotmesis: Involves damage to nerve fibers, resulting in partial loss of function and potential regeneration over time.
- Neurotmesis: The most severe form, causing complete nerve damage and loss of function, often requiring surgical intervention.
Causes of Brachial Plexus Injuries
- Birth Injuries: During complicated deliveries, excessive stretching of the infant’s neck or shoulder region can lead to brachial plexus injuries.
- Trauma: Accidents, falls, or sports-related injuries causing excessive stretching or direct trauma to the shoulder or neck region.
- Tumors or Inflammation: Rarely, tumors or inflammation affecting the brachial plexus can cause nerve damage.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of brachial plexus injuries include numbness, weakness, or loss of sensation in the affected arm or hand. Diagnosis involves a thorough physical examination, imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, and nerve conduction studies to assess nerve function.
Treatment and Rehabilitation
- Conservative Management: Mild cases may recover with time and physical therapy, focusing on exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Surgical Intervention: Severe cases with complete nerve avulsion may require surgical repair or nerve grafting to restore function.
- Occupational Therapy: Rehabilitation programs involving occupational therapy aid in regaining functional abilities and adapting to any lasting limitations.
Prognosis and Recovery
The prognosis for brachial plexus injuries varies based on the severity and extent of nerve damage. Recovery may range from partial to full, often requiring prolonged therapy and follow-up evaluations to monitor progress and adapt treatment strategies.
Brachial plexus injuries, stemming from various causes, can significantly impact an individual’s motor and sensory functions in the affected limb. Timely diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and dedicated rehabilitation efforts play a pivotal role in maximizing recovery and improving the quality of life for individuals affected by these injuries.
